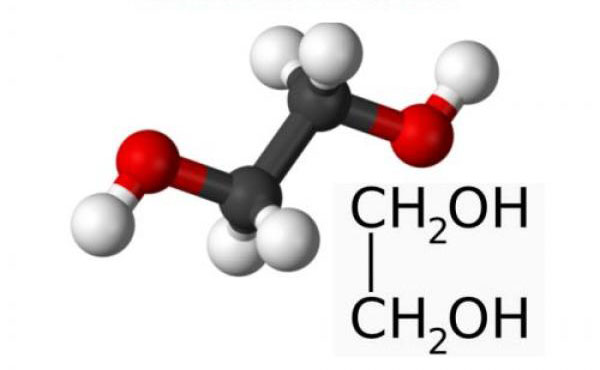
Ethylene glycol (glycol, 1,2-dioxyethane, ethanediol-1,2), HO-CH2-CH2-OH - oxygen-containing organic compound, two-atomic alcohol, the simplest representative of polyols (multiatomic alcohols). Purified form is a transparent colorless liquid of slightly oily consistency. It is odorless and has a sweet taste. Toxic. Entry of ethylene glycol or its solutions into the human body can lead to irreversible changes in the body and to death.
Ethylene glycol is distinguished by its low viscosity and is mixed with water in various proportions, as well as with chemicals: single-atomic and multiatomic alcohols, aromatic and carbonyl compounds, organic acids.
The solution of water and ethylene glycol in the ratio of 1:2 does not freeze at very low temperatures (down to -7000C), and when frozen the solution does not harden, but becomes a loose mass. Such a solution does not expand like ordinary ice, so it does not harm pipes and radiators - this is one of the main features of this substance.
By its nature, the substance is truly amazing, it loves moisture and can absorb it from the atmosphere. If you leave a container filled with ethylene glycol in the open, then in 10 days it will not be a pure substance, and the solution, which consists of 50% of water. And also when mixing this substance with water, a solution is obtained, the volume of which is slightly less than the total volume of the initial components. Ethylene glycol has the lowest freezing point and the lowest viscosity, which makes it easier to pump the coolant through pipes.
Applications:
In the industry ethylene glycol is used as a coolant. With half the heat capacity of water, ethylene glycol absorbs and releases heat much faster, which affects the acceleration of heat transfer. With its high boiling point, ethylene glycol, unlike water, helps to transmit higher temperatures. Radiators of heating, conditioners, chillers, fan coils - for work of this and other equipment solutions in which ethylene glycol contains are applied. Besides, ethylene glycol is used for production of hydraulic fluids.
In antifreeze ethylene glycol is used to reduce freezing point and to avoid crystal formation. Even when freezing in a mixture of ethylene glycol and water, small crystals are formed, which in general are not like solids, but like porridge.
Ethylene glycol is one of the main components in the production of polymers. For example, in the production of PET (polyethylene terephthalate). Depending on the level of polymerization, a wide range of products are produced, from film to plastic mass for transparent bottles.

In the oil industry ethylene glycol is used to dry natural or petroleum gas. Due to its hygroscopic properties, it absorbs water vapour from the gas, thus drying it out and preventing corrosion.
In daily life ethylene glycol can be found in glass cleaners and shoe polishers. It is not the main component, but its hygroscopic properties give the shoes shine and moisture.
In the wood industry ethylene glycol is used as an antiseptic in the fight against mould and decomposition (can be used both to prevent them from being broken down and to remove them). It is one of the cheapest means of stopping the rotting process of wooden ships.
In biology ethylene glycol is used as an alternative to formaldehyde in the preservation of various samples.


